As a member of the Japan Technological Research Association of Artificial Photosynthetic Chemical Process (ARPChem), which was established in October 2012, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation is participating in an Artificial Photosynthesis project being conducted by New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) and pushing forward with joint development in partnership with domestic chemical manufacturers, universities, national institutes and other research institutions.
Artificial photosynthesis utilizes clean hydrogen produced from water using solar energy, and converts carbon dioxide emitted from factories and power plants into basic chemicals that can be used as raw materials for plastics and other products. Aiming at social implementation of artificial photosynthesis, Mitsubishi Chemical is working on technology development for all three stages of artificial photosynthesis.
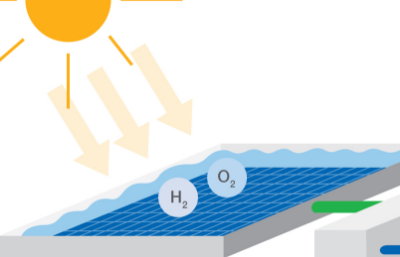
Step One
Hydrogen production from water
The photocatalyst sheet is exposed to light and soaked in water, separating the water into hydrogen and oxygen.

Step Two
Separation of hydrogen and oxygen
Utilize a separation membrane to split hydrogen from the emitted mixed gas, consisting of hydrogen and oxygen.
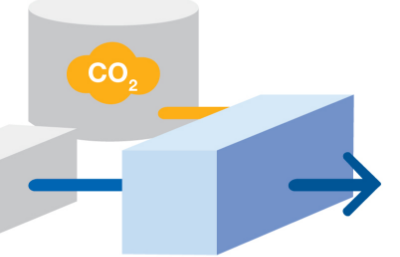
Step Three
Polyolefin production from carbon dioxide
A synthetic catalyst is used to create a reaction between hydrogen and CO2, producing olefins.
Photocatalyst
We are developing photocatalysts with excellent LCA characteristics in hydrogen production. Large-scale demonstration is scheduled for 2030, with social implementation in 2040.
CO2 recyclability catalyst

Mitsubishi Chemical is studying energy saving in the CO2 resource reaction process.
Pilot tests are being conductive of a novel methanol synthesis method using a semilac membrane as a reaction separation membrane.

Contact us today to ask how our environmentally friendly materials can help your product design.